
| | | | |
|
|
| | | | | |
Thrombophysiology: The Logical Study of Blood Clots
Blood Clot Formation
Blood is resin full of red cells, protein, platelets and water that is ever ready to coagulate and form blood clots. Metabolic acid is the hardener that transforms blood resin into blood clot epoxy.
The 'compartment syndrome' from sitting reduces venous blood flow, which depletes tissue oxygen. This changes metabolism and produces metabolic acid that causes blood clot formation. Moreover, metabolic acid causes painful neuropathy and weakness.
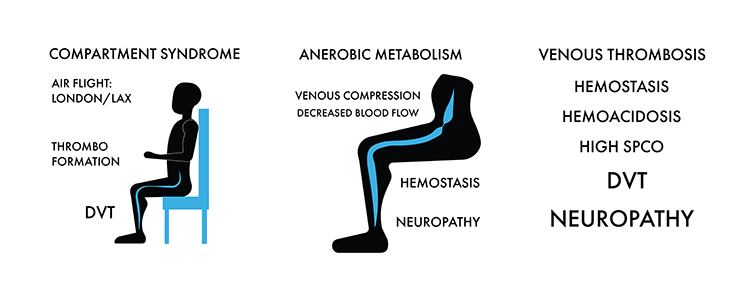
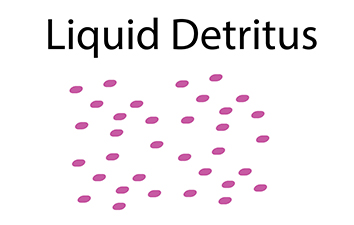
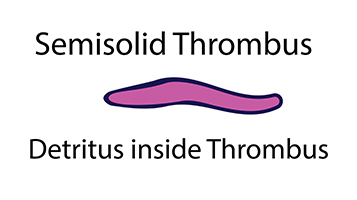
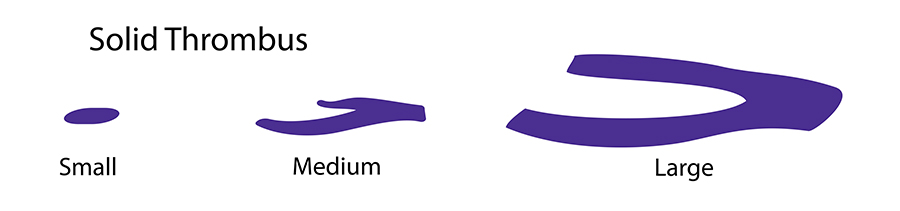
Initially, blood resin forms a loose knit coagulum of polymers that form a purple gel called detritus. Gel changes over time into an organized flexible blood clot called a thrombus. These become semisolid or solid deep venous thrombosis (DVT). Later, small pieces of DVT break loose during exercise or walking, which releases a mixture called venous thromboembolism (VTE), composed of liquid blood clot glue (detritus), semisolid thrombus, or solid thrombus into venous circulation. VTE migrate into the heart and cause palpitations with arrhythmias.
 |
 |
|---|
Blood clots inside the right atrium cause fast fluttering sensations with weak fluttering jugular palpitations (pulsus reversus), and blood clots in the right ventricle cause slow flip-flop sensations with skipped heartbeats (pulsus interruptus) as VTE pass through the pulmonary valve.
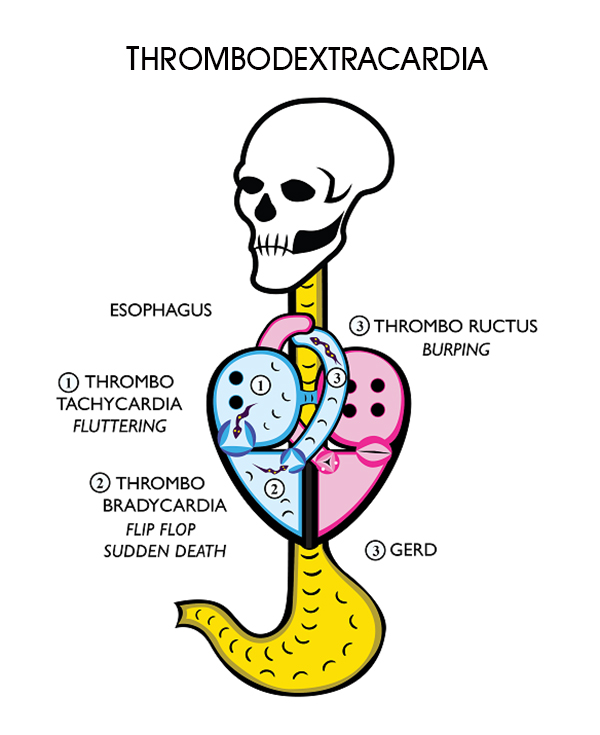
Thrombodextracardia: Venous Thrombo Embolism (VTE) of the Heart
Semisolid and solid venous blood clots interfere with blood flow through the valves, which causes palpitations and arrhythmias. Thrombodextrcardia, VTE Moreover, clots accumulate inside the pulmonary artery at the esophagus, which compresses and interferes with swallowing. This causes nausea and burping (thrombo-ructus) and burping while sleeping causes gastro esophageal reflux disease (GERD).
Sick Sinus Syndrome = Thrombo Tachycardia + Thrombo Bradycardia
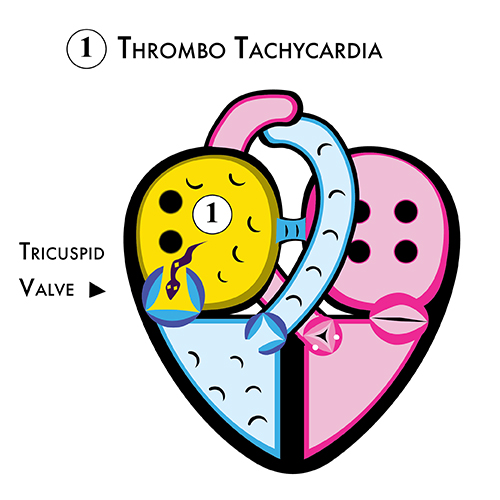
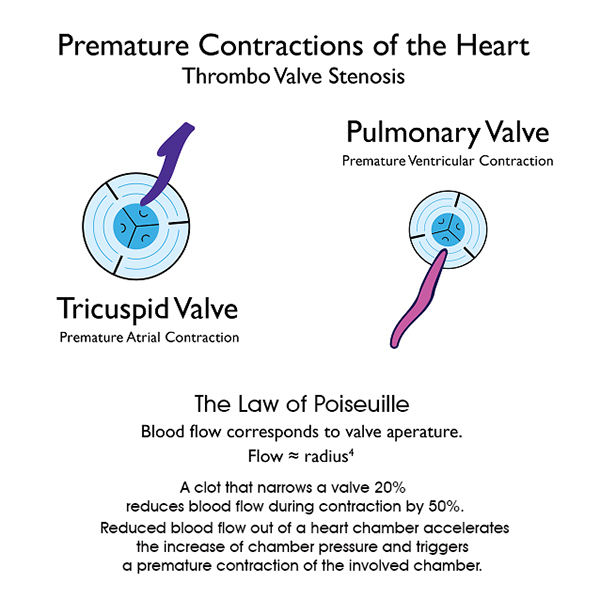
Clots inside the right atrium cause pulsus reversus (jugular venous pulsations), premature atrial contractions, atrial flutter, and atrial fibrillation.
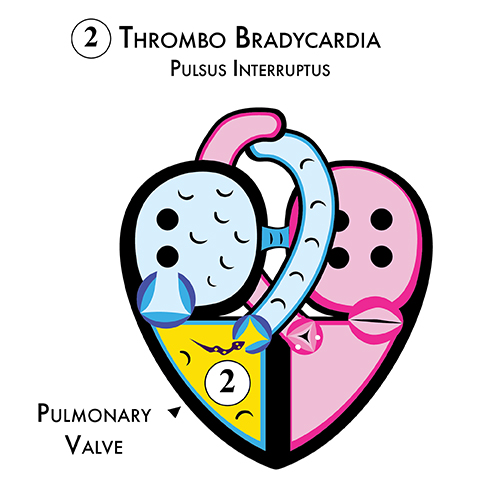
Blood clots inside the right ventricle obstruct the pulmonary valve, which causes premature ventricular contractions, bigeminy, bradycardia, pulsus interruptus (skipped heartbeats). Continuous skipped beats lead to fainting spells, seizures, and sudden cardiac arrest.
Thrombo-Ructus causes Gastro Esophageal Reflux Disease
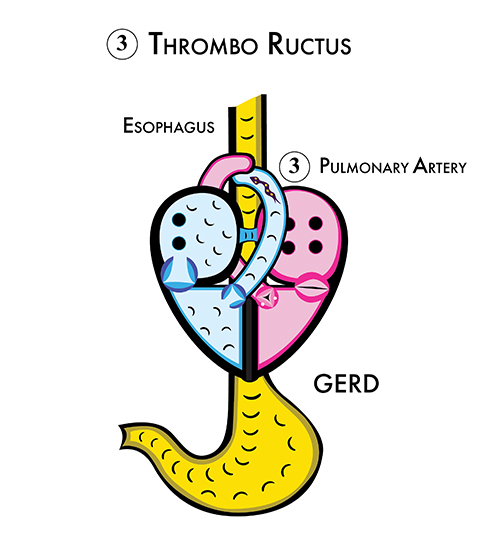
Blood clots accumulate inside the pulmonary artery next to the esophagus and thrombo irritation of the esophagus causes nausea, gagging, burping, and vomiting. Burping while sleeping causes gastro esophageal reflux disease (GERD).
CPR for Thrombocardiac Arrest
Cardio Pulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) reanimates an unconscious person with a pulseless electrocardiogram by unclogging the pulmonary valve, which is occluded by a solid blood clot inside the pulmonary valve.
- Long blood clots in the pulmonary valve stop blood flow into the lungs and brain
- Sudden thrombogenic cardiac arrest causes hypoxic acidosis
- Brain acidosis stops neurotransmission and causes unconsciousness
- Brain acidosis triggers unconscious anoxic convulsive reflexes
- Epileptic convulsions perform unconscious CPR for thrombogenic seizures